bipv solar
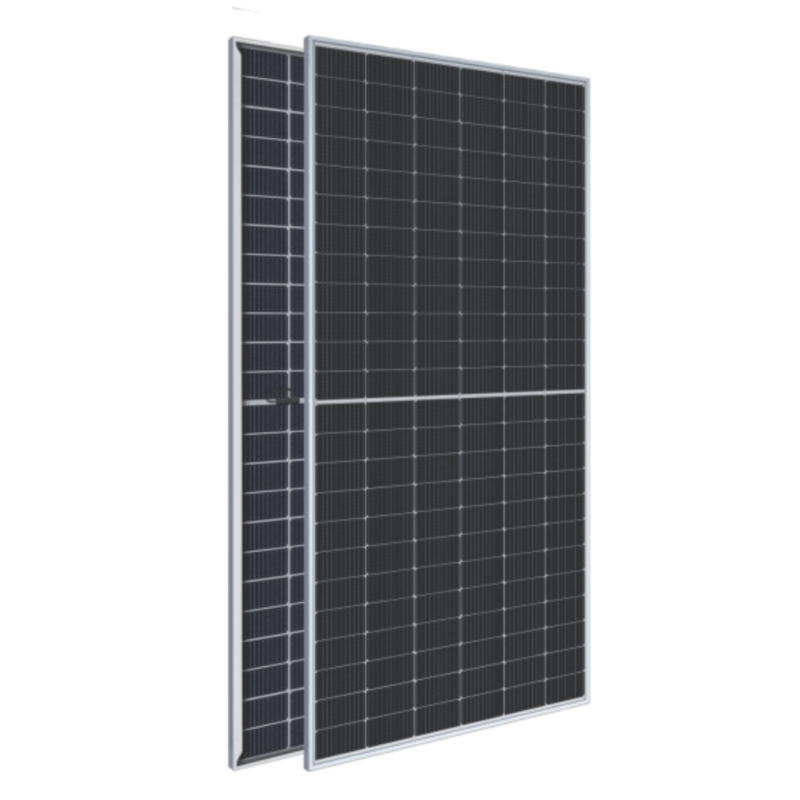
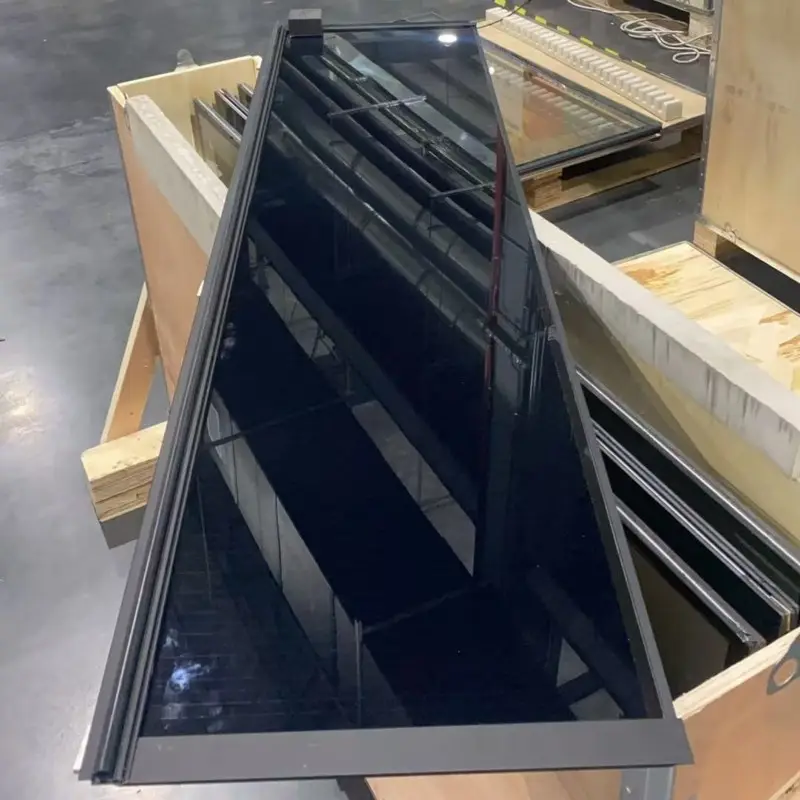
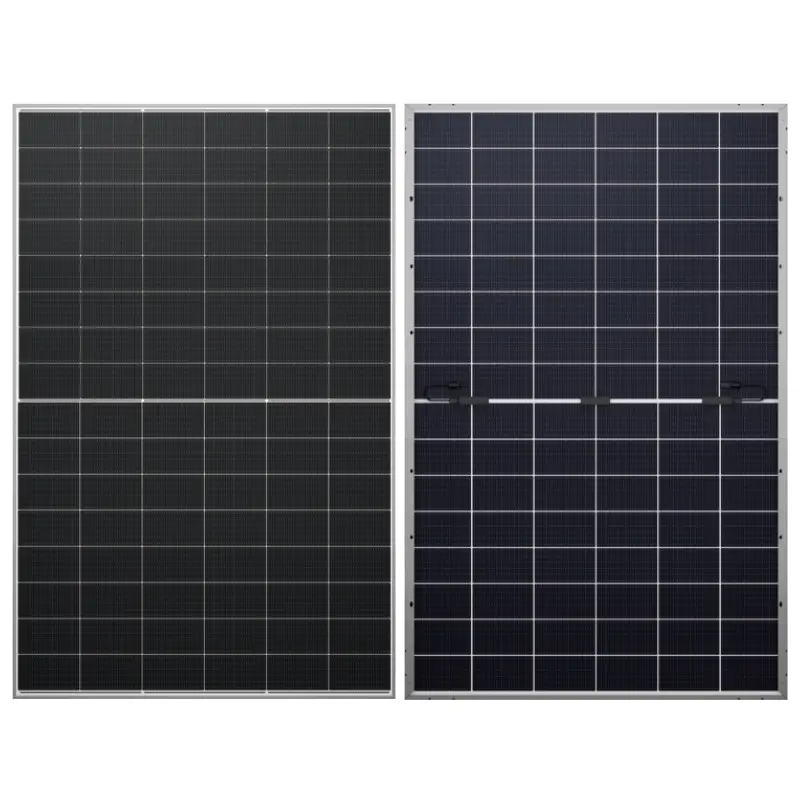
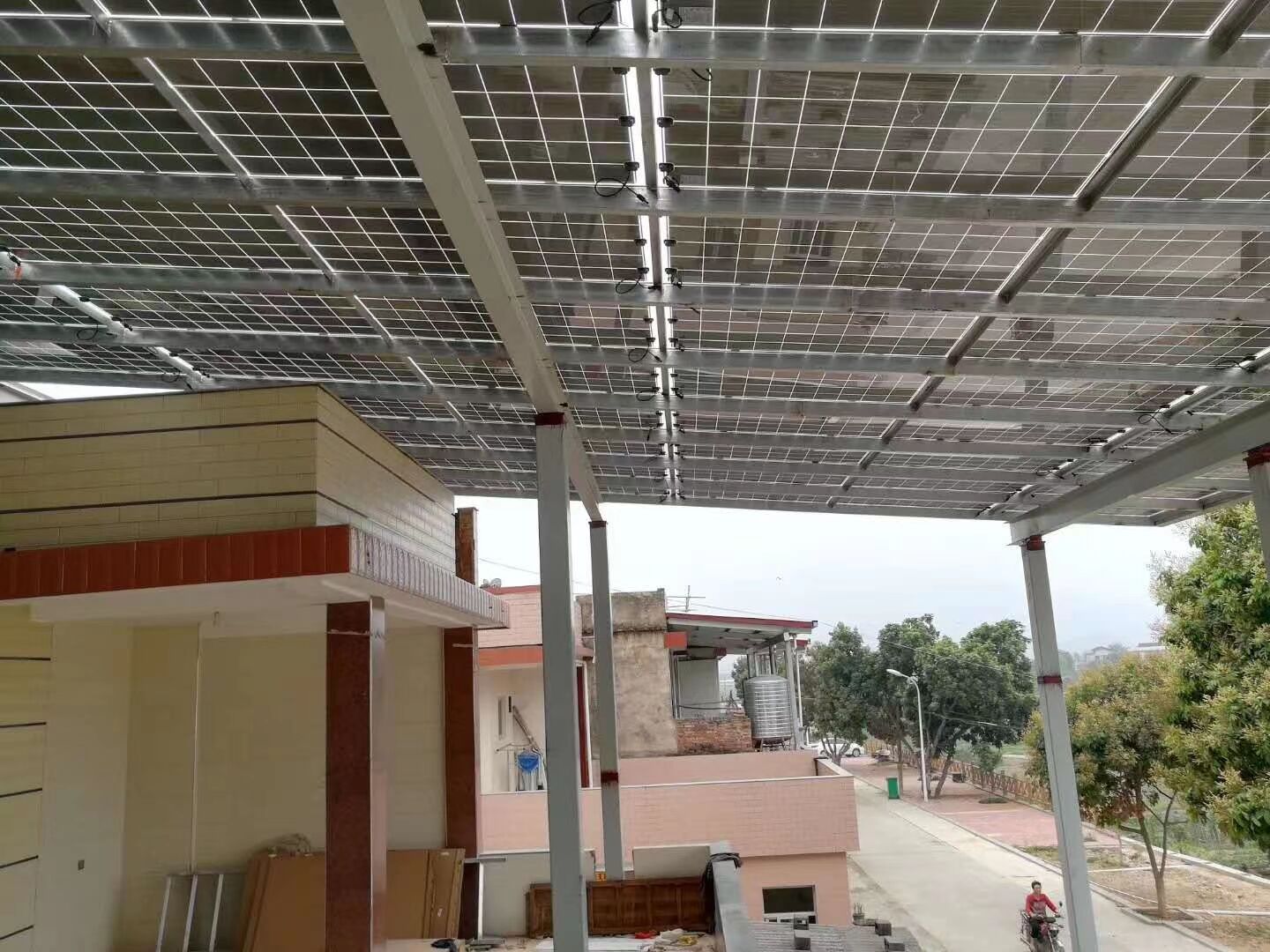
Building Integrated Photovoltaic (BIPV) solar systems represent a revolutionary advancement in sustainable energy technology, seamlessly combining architectural functionality with renewable power generation. Unlike traditional solar panels that are mounted on top of existing structures, BIPV solar solutions are integrated directly into building materials, serving dual purposes as both construction elements and electricity generators. This innovative approach transforms roofs, facades, windows, and other building components into active energy-producing surfaces while maintaining aesthetic appeal and structural integrity. BIPV solar technology encompasses various forms, including photovoltaic roof tiles, solar glass panels, transparent solar cells for windows, and facade-mounted systems that replace conventional building materials. The core functionality centers on converting sunlight into electrical energy through photovoltaic cells embedded within building components. These systems utilize crystalline silicon, thin-film, or emerging perovskite technologies to achieve efficient energy conversion while meeting architectural requirements. The technological features of BIPV solar include weatherproofing capabilities, thermal insulation properties, and customizable designs that match specific architectural aesthetics. Modern BIPV solar installations incorporate smart monitoring systems, enabling real-time performance tracking and optimization. Applications span residential homes, commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and public infrastructure projects. Residential BIPV solar installations commonly feature integrated roof tiles and solar windows, while commercial applications often utilize large-scale facade systems and canopy structures. The technology proves particularly valuable in urban environments where space constraints limit traditional solar panel installations. Educational institutions, hospitals, shopping centers, and office buildings increasingly adopt BIPV solar solutions to reduce energy costs and carbon footprints. Government buildings and public facilities also embrace this technology to demonstrate environmental leadership and achieve sustainability goals while maintaining architectural standards and municipal design requirements.